284461-73-0
- Product Name:Sorafenib int
- Molecular Formula:C21H16ClF3N4O3
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:464.831
Product Details
Trustworthy Manufacturer Supply Buy Quality Sorafenib int 284461-73-0 with Efficient Transportation
- Molecular Formula:C21H16ClF3N4O3
- Molecular Weight:464.831
- Appearance/Colour:light yellow solid
- Vapor Pressure:4.76E-11mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:202-204 °C
- Boiling Point:523.3 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:12.89±0.70(Predicted)
- Flash Point:270.3 °C
- PSA:92.35000
- Density:1.454 g/cm3
- LogP:6.08660
Sorafenib tosylate(Cas 284461-73-0) Usage
|
Uses |
Sorafenib, an orally active potent multi-kinases inhibitor,was approved in the U.S. for the treatment of advanced renalcell carcinoma. The drug targets both tumor cell proliferationand tumor angiogenesis kinases that include RAF,VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, PDGFR-??, KIT and FLT-3. Sorafenibis being jointly developed by Bayer and Onyx in phase IIItrials as a single agent for the treatment of advanced hepato-cellular carcinoma and in combination with carboplatin andpaclitaxel in patients with advanced metastatic melanoma.Phase II trials in combination with doxorubicin for thetreatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma are alsounder investigation. Additional phase II trials are ongoingfor non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and in postmenopausalwomen with estrogen receptor and/or progesteronereceptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. In addition, theNational Cancer Institute (NCI) is evaluating the compoundboth as a single therapy agent and in combination with otheroncology agents in phase II trials for several cancer indications. |
|
Overview |
Sorafenib tosylate is the tosylate form of sorafenib, which is a drug approved for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma and the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (primary kidney cancer). Hepatocellular carcinoma accounts for the vast majority of primary liver cancers (85–90%). [1] Approximately 70–90% of all hepatocellular cancer cases occur in patients with chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, with the main causes of cirrhosis including hepatitis B, hepatitis C and alcoholic liver disease.[1] Sorafenib is an oral receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits Raf serine/threonine kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases (vascular endothelial growth factor receptors 1, 2, 3 and platelet-derived growth factor-b, Flt-3 and c-kit) that are implicated in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Figure 1 the chemical structure of sorafenib; |
|
Indications |
It is indicated for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma and the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (primary kidney cancer). |
|
Mechanism of action |
The bi-aryl urea sorafenib is an oral multikinase inhibitor that inhibits both cell surface tyrosine kinase receptors and downstream intracellular serine/threonine kinases in the Ras/MAPK cascade.[2-4] Receptor tyrosine kinases inhibited by sorafenib include vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-1, VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR)-b, c-KIT, FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT-3) and RET. Intracellular Raf serine/threonine kinase isoforms inhibited by sorafenib include Raf-1 (or C-Raf), wild-type B-Raf and mutant B-Raf.[3, 4] These kinases are involved in tumour cell proliferation and tumour angiogenesis.[3, 4] The antiproliferative activity of sorafenib is variable in different tumor types and largely depends on the oncogenic signaling pathways that mediate tumor proliferation. Sorafenib has also been shown to induce apoptosis in several tumor cell lines. Although the mechanism through which sorafenib induces apoptosis is not fully elucidated and may vary between cell lines, a commonly observed theme is the inhibition of phosphorylation of the initiation factor eIF4E and loss of the antiapoptotic protein myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL-1)[5]. Recently, sorafenib was shown to inhibit hepatitis C viral replication in vitro[6], and in vitro studies have also shown some direct effects on immune cells [7]. Whether these effects |
|
Side effects |
The most common adverse reactions (20%), considered to be related to sorafenib, in patients with HCC or RCC are fatigue, weight loss, rash/desquamation, hand-foot skin reaction, alopecia, diarrhea, anorexia, nausea and abdominal pain [12]. Across all tumor types, common side effects (> 10%) include hypertension (9 -13%, grade 4: < 1%; onset: ~ 3 weeks), fatigue (37 -46%), sensory neuropathy (13%), pain (11%), rash/desquamation (19 -40%; grade 3: 1%), handfoot syndrome (21 -30%; grade 3: 6 -8%), alopecia (14 -27%), pruritis (14 -19%), dry skin (10 -11%), hypoalbuminemia (59%), hypophosphatemia (35 -45%; grade 3: 11 -13%; grade 4: < 1%), diarrhea (43 -55%; grade 3: 2 -10%; grade 4: < 1%), lipase increased (40 -41%, usually transient), amylase increased (30 -34, usually transient), abdominal pain (11 -31%), weight loss (10 -30%), anorexia (16 -29%), nausea (23 -24%), vomiting (15 -16%), constipation (14 -15%), muscle pain, weakness, dyspnea (14%), cough (13%) and hemorrhage (15 -18%; grade 3: 2 -3%; grade 4: 2%). Laboratory abnormalities attributable to sorafenib use are also seen and include lymphopenia (23 -47%; grades 3/4: 13%), thrombocytopenia (12 -46%; grades 3/4: 1 -4%), international normalized ration (INR) increased (42%), neutropenia (18%; grades 3/4: 5%), leucopenia, liver dysfunction (11%; grade 3: 2%; grade 4: 1%). Less frequent side effects (> 1 -10) include cardiac ischemia/infarction (3%), flushing, headache (10%), depression, fever, acne, exfoliative dermatitis, decreased appetite, dyspepsia, dysphagia, esophageal varices bleeding (2%), glossodynia, mucositis, stomatitis, xerostomia, erectile dysfunction, anemia, transaminases increased (transient), joint pain (10%), arthralgia, myalgia, hoarseness and flu-like syndrome. Rare (< 1%) side effects of sorafenib include acute renal failure, alkaline phosphatase increased, arrhythmia, bilirubin increased, bone pain, cardiac failure, cerebral hemorrhage, congestive heart failure, dehydration, eczema, epistaxis, erythema multiforme, folliculitis, gastritis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal perforation, gastrointestinal reflux, gynecomastia, hypersensitivity (skin reaction, urticaria), hypertensive crisis, hyponatremia, hypothyroidism, infection, jaundice, myocardial infarction (MI), mouth pain, myocardial ischemia, pancreatitis, pleural effusion, preeclampsialike syndrome (reversible hypertension and proteinuria), renal failure, respiratory hemorrhage, reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS), rhinorrhea, skin cancer (squamous cell/keratoacanthomas), thromboembolism, tinnitus, transient ischemic attack, tumor lysis syndrome, tumor pain and voice alteration. |
|
Description |
Sorafenib is a small molecular inhibitor of several kinases involved in tumor angiogenesis and proliferation, including, but not limited to, Raf (IC50=12nM for Raf-1), VEGFR (IC50=90nM for VEGFR-2 and IC50=12nM for VEGFR-3), and platelet derived growth factor receptor (IC50=57nM for PDGFR-b). Specifically, sorafenib blocks tumor progression by inhibiting cellular proliferation that is dependent on activation of the MAPK pathway (Raf) and/or inhibiting tumor angiogenesis through VEGFR and/or PDGFR. While it may be effective in the treatment of a variety of tumors, the first approvable indication is for renal cell carcinoma. Overall, the drug appears to be well tolerated by the majority of patients at the 400 mg b.i.d. continuous dosing. As an inhibitor of multiple kinases vital for tumor progression, sorafenib may possess wide-spectrum antitumor properties and may emerge as an effective weapon against a variety of solid tumors. |
|
Chemical Properties |
Light Yellow Solid |
|
Originator |
Bayer/Onyx (Germany) |
|
Brand name |
Nexavar (Bayer HealthCare); Xarelto (Bayer HealthCare). |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Clinical Use |
Protein kinase inhibitor: Treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma Treatment of thyroid cancer |
|
Synthesis |
An improved, four-step synthesis in 63% overall yield was published recently and is illustrated in the scheme. Picolinic acid (127) was heated with Vilsmeier reagent for 16 hr to give 128 in 89% yield as an off-white solid. The acid chloride 128 was treated with methylamine in methanol at low temperature to give amide 129 in 88% yield as paleyellow crystals after its crystallization from ethyl acetate.4-Aminophenol anion was generated under a basic condition and compound 129 was added to the anion solution to give corresponding addition compound 131 in 87% yield. For an unknown reason, potassium carbonate used in the reaction increased the reaction rate significantly. Finally, compound 131 was condensed with isocyanate 132 in methylene chloride to give sorafenib (XVIII) in 92% yield as a white solid. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Anticoagulants: may enhance effect of coumarins. Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine (increased risk of agranulocytosis). Antivirals: avoid with boceprevir. |
|
Metabolism |
Sorafenib is metabolised primarily in the liver and undergoes oxidative metabolism mediated by CYP3A4, as well as glucuronidation mediated by UGT1A9. 8 metabolites have been identified, during in vitro studies one has been shown to have equal activity to sorafenib. About 96% of a dose is excreted within 14 days, with 77%, mostly as unchanged drug, recovered in the faeces, and 19% in the urine as glucuronidated metabolites. |
InChI:InChI=1/C21H16ClF3N4O3.C7H8O3S/c1-26-19(30)18-11-15(8-9-27-18)32-14-5-2-12(3-6-14)28-20(31)29-13-4-7-17(22)16(10-13)21(23,24)25;1-6-2-4-7(5-3-6)11(8,9)10/h2-11H,1H3,(H,26,30)(H2,28,29,31);2-5H,1H3,(H,8,9,10)
284461-73-0 Relevant articles
Identification of Diarylurea Inhibitors of the Cardiac-Specific Kinase TNNI3K by Designing Selectivity against VEGFR2, p38α, and B-Raf
Cheung, Mui,Desai, Tina A.,Fries, Harvey,Gatto, Gregory J.,Graves, Alan P.,Holt, Dennis A.,Kallander, Lara S.,Patterson, Jaclyn R.,Shewchuk, Lisa,Stoy, Patrick,Totoritis, Rachel,Wang, Liping
, p. 15651 - 15670 (2021/11/16)
A series of diarylurea inhibitors of the...
Synthesis, anticancer activity, and β-lactoglobulin binding interactions of multitargeted kinase inhibitor sorafenib tosylate (SORt) using spectroscopic and molecular modelling approaches
Tanzadehpanah, Hamid,Bahmani, Asrin,Hosseinpour Moghadam, Neda,Gholami, Hamid,Mahaki, Hanie,Farmany, Abbas,Saidijam, Massoud
, p. 117 - 128 (2020/08/19)
Sorafenib tosylate (SORt) is an oral mul...
Catalytic Decarboxylative C?N Formation to Generate Alkyl, Alkenyl, and Aryl Amines
Zhang, Yipin,Ge, Xia,Lu, Hongjian,Li, Guigen
supporting information, p. 1845 - 1852 (2020/12/01)
Transition-metal-catalyzed sp2 C?N bond ...
Sorafenib hemicamsylate and processes for preparation thereof
-
Paragraph 0082-0086, (2020/05/26)
The present invention relates to: novel ...
284461-73-0 Process route
-
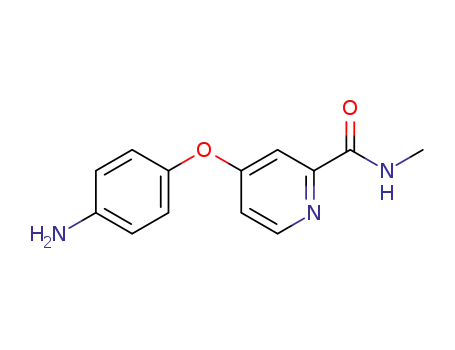
- 284462-37-9
4-(4-aminophenoxy)-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide
-
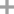
- 327-78-6
4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl isocyanate

-
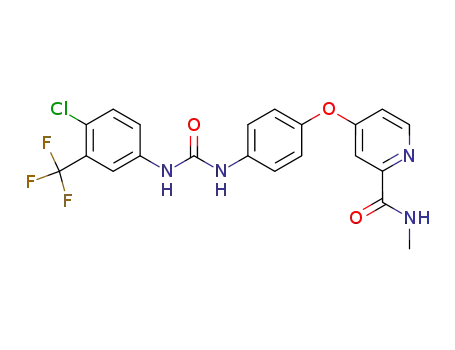
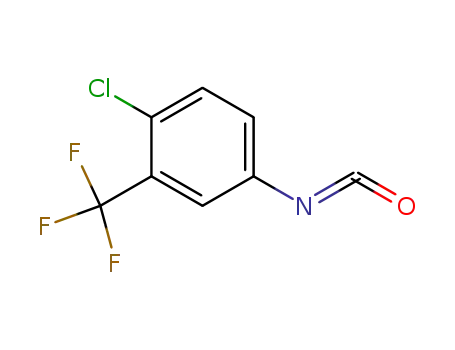
- 284461-73-0
sorafenib
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With zirconia grinding balls; In acetonitrile; for 4h; Milling;
|
96% |
|
In ethyl acetate; at 20 - 30 ℃; Large scale;
|
94.2% |
|
In dichloromethane;
|
93% |
|
In dichloromethane;
|
93% |
|
In dichloromethane;
|
93% |
|
In dichloromethane;
|
93% |
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃;
|
93% |
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 22h;
|
93% |
|
In ethyl acetate; at 20 - 60 ℃; for 1.5h; Industry scale;
|
93% |
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 22h;
|
93% |
|
In ethyl acetate; at 20 - 60 ℃; for 1.5h;
|
93% |
|
In dichloromethane; for 24h;
|
93% |
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 22h;
|
93% |
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; Inert atmosphere;
|
92% |
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 ℃; for 17h; Inert atmosphere;
|
90% |
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 70h;
|
87.5% |
|
With N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine; In dichloromethane; for 10h;
|
85% |
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 12h;
|
80% |
|
In butanone; at 80 - 85 ℃;
|
75% |
|
In butanone; at 25 - 85 ℃;
|
75% |
|
With triethylamine; In N,N-dimethyl-formamide; at 20 ℃;
|
54% |
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 16.5h;
|
52.3% |
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 0.16h;
|
52.3% |
|
In dichloromethane;
|
|
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 22h;
|
|
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 ℃; for 22h;
|
|
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 22h;
|
|
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 22h;
|
|
|
In dichloromethane; at 0 - 20 ℃;
|
8.6 g |
|
In Isopropyl acetate; at 0 - 70 ℃; for 5.5h; Solvent; Temperature;
|
79.11 g |
-
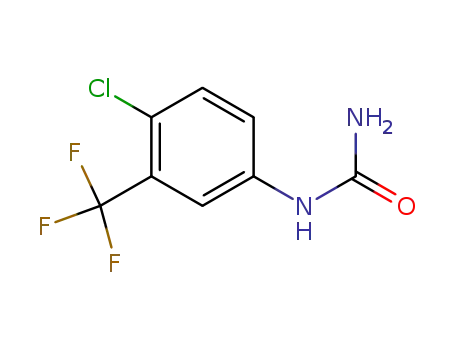
- 343247-69-8
4-chloro-3-trifluoromethylphenylurea

-
![[4-(4-bromophenoxy)(2-pyridyl)]-N-methylcarboxamide](/upload/2024/4/b7a06733-e9db-4844-b8f6-d0ac5f5eb3f1.png)
- 1154243-75-0
[4-(4-bromophenoxy)(2-pyridyl)]-N-methylcarboxamide

-

- 284461-73-0
sorafenib
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
[4-(4-bromophenoxy)(2-pyridyl)]-N-methylcarboxamide; With potassium phosphate; tris-(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0); 4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene; In 1,4-dioxane; at 20 ℃; for 0.5h;
4-chloro-3-trifluoromethylphenylurea; In 1,4-dioxane; at 80 - 100 ℃; for 1h; Solvent; Reagent/catalyst;
|
97.9% |
|
With t-BuBrettPhos; palladium diacetate; caesium carbonate; In tetrahydrofuran; water; at 75 ℃; for 5h; Inert atmosphere;
|
206 mg |
284461-73-0 Upstream products
-
284462-37-9

4-(4-aminophenoxy)-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide
-
327-78-6

4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl isocyanate
-
2056030-06-7
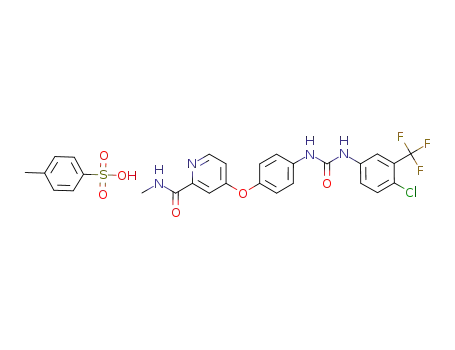
sorafenib tosylate
-
1129683-83-5
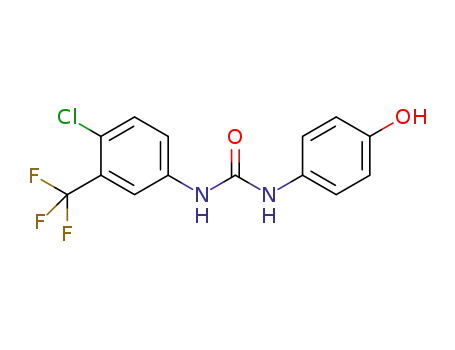
4-[ ({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}carbonyl)amino]phenol
284461-73-0 Downstream products
-
583840-03-3
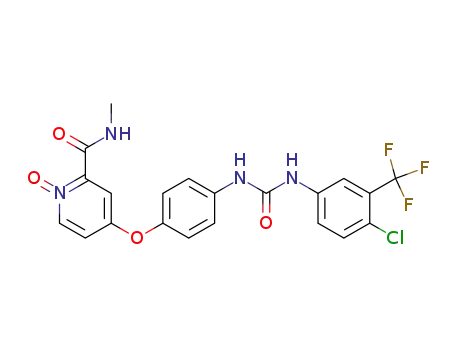
BAY 67-3472
-
2056030-06-7

sorafenib tosylate
-
2056030-06-7
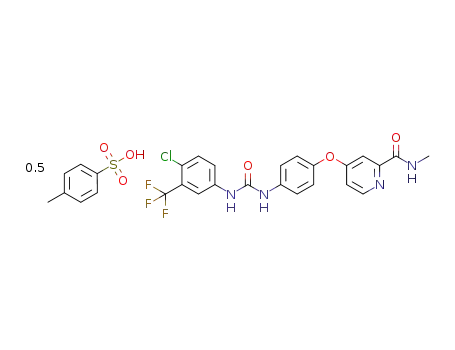
4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)phenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide semi-4-methylbenzenesulfonate
-
2056030-06-7
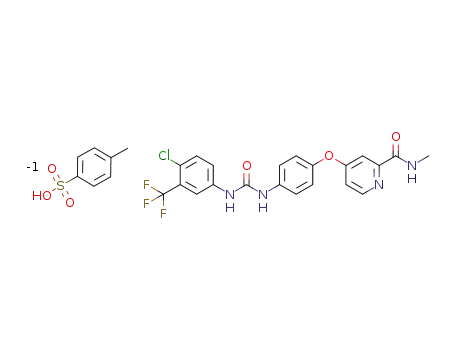
N-[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N′-[4-[2-(N-methylcarbamoyl)-4-pyridyloxy]phenyl]urea p-toluenesulfonate
Relevant Products
-
Gefitinib int
CAS:184475-35-2
-
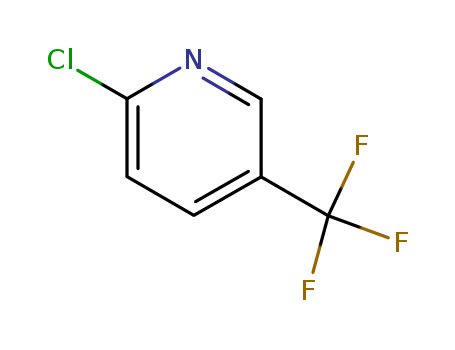
2-Chloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridine
CAS:52334-81-3
-
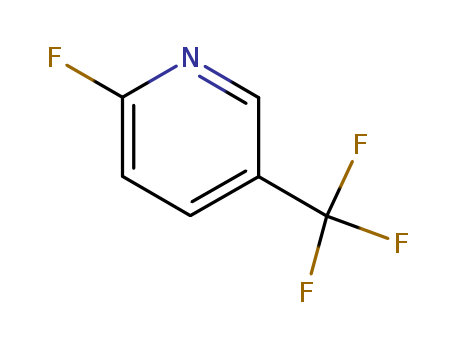
2-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine
CAS:69045-82-5