184475-35-2
- Product Name:Gefitinib int
- Molecular Formula:C22H24ClFN4O3
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:446.909
Product Details
Reputable Manufacturer Supply Factory Sells Gefitinib int 184475-35-2 with Reasonable Price
- Molecular Formula:C22H24ClFN4O3
- Molecular Weight:446.909
- Appearance/Colour:light-yellow crystalline powder
- Vapor Pressure:0mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:119-120 °C
- Refractive Index:1.621
- Boiling Point:586.8 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:7.00±0.10(Predicted)
- Flash Point:308.7 °C
- PSA:68.74000
- Density:1.322 g/cm3
- LogP:4.28650
Gefitinib(Cas 184475-35-2) Usage
|
Mechanism of Action |
Gefitinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor used in targeted treatment for malignant conditions, particularly non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling by binding to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) sites, leading to suppression of downstream signaling cascades that promote tumor cell proliferation. |
|
Therapeutic Use and Approval |
Approved in several countries globally as second-line and third-line treatment for NSCLC. Often used as a first-line therapeutic strategy for NSCLC. |
|
Pharmacokinetics |
Belongs to Biopharmaceutics Classification System class II. |
|
Combination Therapy and Nanoparticles |
Used in combination with other therapeutic agents like natural compounds, small interfering RNA, and in photodynamic therapy to enhance efficacy. |
|
Clinical Trial Data |
Gefitinib is well tolerated in patients with various tumor types. Demonstrates anti-proliferative and anti-tumoral activity, particularly in breast cancer (BC). |
|
Challenges and Limitations |
Gefitinib has low solubility, delayed absorption, and low bioavailability, leading to significant side effects. Its therapeutic application is limited due to unavoidable side effects and the availability of alternative treatments for lung cancer. |
|
Future Directions |
Understanding cellular targets of gefitinib can aid in predicting outcomes and overcoming resistance in certain tumor types, such as TNBC. |
|
Indications and Uses |
Gefitinib is an antineoplastic target therapy drug with relatively high specificity that was developed by the British pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca; it is the first molecular targeted drug to be used in non-small cell lung cancer treatment. Epidermal growth factors (EGF) are a kind of polypeptide with a relative molecular mass of 6.45x103, and they can bind with epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) on target cell membrane surfaces to trigger biological effects. EGFR is a type of tyrosine kinase (TK) type receptor, so when bound with EGF, it will promote TK activation in the receptor. This will cause tyrosine residue in the receptor to autophosphorylate and send continuous dividing signals into the cell, causing cell proliferation and differentiation. EGFR is abundant in human tissue, and it is highly expressed in malign tumors. Gefitinib blocks the signal transduction pathway of cell surface EGFR to prevent tumor growth, metastasis, and growth in blood vessels, and it can induce tumor cell apoptosis. Gefitinib is mainly used to treat non-stem cell lung cancer. |
|
Adverse Reactions |
Gefitinib is relatively well-tolerated, and most negative reactions are mild and reversible, characteristics that are vastly different from those of standard negative reactions to cytotoxic drugs. Common negative reactions include diarrhea, nausea, rashes, acne, vomiting, and feebleness. Only 1% of patients have had to cease treatment due to negative reactions with an occurrence rate over 20%. There have also been rare cases of acute interstitial pneumonia. |
|
Warnings and precautions |
Gefitinib is not suitable for pregnant women, and breastfeeding women should cease breastfeeding throughout their treatment period. |
|
Description |
Gefitinib was introduced in Japan as a daily oral monotherapy for the treatment of inoperable or recurrent non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC). This anilinoquinazoline derivative can be synthesized in 6 steps starting from 6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4(3H)-one by successive monodemethylationlacetylation of the 6-hydroxy-group followed by chlorination and reaction with 3-chloro-4-fluoroaniline, finally deacetylation and alkylation with 3-(4-morpholinyl)propylbromide complete the synthesis. Gefitinib reversibly inhibits the activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGRF TK). This inhibits autophosphorylation of EGRF and blocks the cascade of intracellular events which have been implicated in the proliferation, survival and metastasis of cancer cells. Gefitinib diplays good selectivity for the EGRF TK relative to other growth factors in human umbilical endothelial cells. It is similarly selective relative to other kinases, for example cerB2. Data from two large phase II studies in patients with pretreated NSCLC have shown that gefitinib induces a response rate approaching 20% in patients receiving the agent as a second line therapy and approximately 10% in those pretreated with more lines of chemotherapy. Gefitinib has good bioavailability and is metabolized in the liver via the cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme system with a mean elimination half life of 28 h. Gefitinib has been generally well tolerated in cancer patients with predominant side effects being acne-like skin-rash, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and mild to moderate myelosuppression. . |
|
Chemical Properties |
Light-Yellow Crystalline Powder |
|
Originator |
Astra Zeneca (UK) |
|
Uses |
Gefitinib (Iressa, ZD-1839) is an EGFR inhibitor for Tyr1173, Tyr992, Tyr1173 and Tyr992 in the NR6wtEGFR and NR6W cells with IC50 of 37 nM, 37nM, 26 nM and 57 nM, respectively. |
|
Indications |
Iressa (ZD1839) is an orally active tyrosine kinase inhibitor selective for the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor tyrosine kinase. Iressa is undergoing clinical trials in the treatment of various solid tumors, including head and neck cancer, breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. Its antitumor activity is derived from the fact that the EGF receptor and EGF signaling are frequently overactivated in sensitive tumors. The major side effects include diarrhea and skin rash. Bone marrow toxicity has not been a dose-limiting problem. |
|
Brand name |
Iressa (AstraZeneca). |
|
General Description |
Geftinib is available as 250-mg tablets for oral administrationin the treatment of NSCLC for those patients who have failedto respond to platinum-based therapies and docetaxel and hasalso been used against squamous cell cancers of the head andneck. The agent is an inhibitor of the TK of EGF-R and possiblyother TKs as well. Gefitinib is both a substrate and inhibitorof Pgp and BCRP. The agent is absorbed slowly afterbeing administered orally with 60% bioavailability.Metabolism occurs in the liver and is mediated primarily byCYP3A4 to give eight identified metabolites resulting fromdefluorination of the phenyl ring, oxidative-O-demethylation,and multiple products arising as a result of oxidation of themorpholine ring. The O-demethylated product represents thepredominate metabolite and is 14-fold less active comparedwith the parent. The parent and metabolites are eliminated inthe feces with a terminal elimination half-life of 48 hours.The drug appears to be well tolerated with the most commonlyreported side effects being rash and diarrhea. It mayalso cause elevations in blood pressure especially in those patientswith preexisting hypertension, elevation of transaminaselevels, and mild nausea and mucositits. |
|
Biological Activity |
Orally active, selective inhibitor of EGFR tyrosine kinase (IC 50 = 23-79 nM). Shows minimal activity against ErbB2, KDR, c-flt, PKC, MEK and ERK-2. Blocks EGFR autophosphorylation and inhibits tumor growth in mice bearing a range of human xenografts. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Gefitinib is a selective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGFR TK) inhibitor. Gefitinib has antineoplastic activity, and has been approved for the treatment on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Gefitinib has a higher affinity for ATP (adenosine triphosphate) binding site in the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain than ATP. Hence, gefitinib is known to inhibit the progression of endometrial cancer. |
|
Clinical Use |
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer |
|
Synthesis |
A mixture of 4,5-dimethoxyanthranilic acid (133) and formamide was heated to generate the cyclized quinazoline 134. The quinazoline was selectively monodemethylated with methionine in refluxing methanesulfonic acid to afford 135 in 47% yield. Compound 135 was acylated to give acetate 136, which was treated with refluxing thionyl chloride to yield chloropyrimidine 137. Chloride 137 was condensed with 3-chloro-4-fluoroaniline (138) in refluxing IPA to yield anilinoquinazoline 139 in 56% yield from 136. The acetate protecting group in compound 139 was hydrolyzed with ammonium hydroxide in methanol, and the free phenol was alkylated with 3-(4- morpholinyl)propyl chloride (140) to give gefitinib (13) in 55% yield. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Antibacterials: Avoid with rifampicin (reduced gefitinib concentration). Anticoagulants: possibly enhanced anticoagulant effect with warfarin Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine (increased risk of agranulocytosis). Antivirals: avoid with boceprevir. Ulcer-healing drugs: concentration reduced by ranitidine. Avoid concomitant use with other inhibitors or inducers of CYP3A4. Dose alterations may be required. |
|
Metabolism |
Extensively metabolised in the liver, mainly by the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2D6; the major metabolite is O-desmethylgefitinib, which is much less potent than gefitinib, and unlikely to contribute to its clinical activity. Gefitinib is excreted mainly as metabolites via the faeces (86%); renal elimination of gefitinib and its metabolites accounts for <4% of the dose. |
InChI:InChI=1/C22H24ClFN4O3/c1-29-20-13-19-16(12-21(20)31-8-2-5-28-6-9-30-10-7-28)22(26-14-25-19)27-15-3-4-18(24)17(23)11-15/h3-4,11-14H,2,5-10H2,1H3,(H,25,26,27)
184475-35-2 Relevant articles
Novel preparation of gefitinib
Zheng, Youguang,Li, Mingdong,Zhang, Shaoning,Ji, Min
, p. 388 - 390 (2009)
A new synthesis of the anticancer drug g...
Synthesis of gefitinib from methyl 3-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzoate
Ming, Dong Li,You, Guang Zheng,Ji, Min
, p. 673 - 678 (2007)
This paper reports a novel synthesis of ...
Improved protocol for synthesis of N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy) quinazolin-4-amine (gefitinib)
Kumar, Pawan,Mazlee, Muhammad Taufiq F.,Abdul Wahab, Muhammad K.,Belwal, Chandra Kant,Kumar, Ramesh,Sajid, Shahnawaz
, p. 39 - 46 (2019)
An improved three-step process for the s...
Synthesis of [11C]Iressa as a new potential PET cancer imaging agent for epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
Wang, Ji-Quan,Gao, Mingzhang,Miller, Kathy D.,Sledge, George W.,Zheng, Qi-Huang
, p. 4102 - 4106 (2006)
Iressa (Gefitinib) is an orally active i...
A new synthesis of gefitinib
Maskrey, Taber S.,Kristufek, Tyler,Laporte, Matthew G.,Nyalapatla, Prasanth R.,Wipf, Peter
, p. 471 - 476 (2019)
A four-step synthesis of the FDA-approve...
A Different Approach to the EGFR Inhibitor Gefitinib Involving Solid-Phase Synthesis
Sequeira, André,Louren?o, Ana,Ferreira, Luísa Maria,Branco, Paula Sério,Mendes, Zita,Louren?o, Nuno M. T.,Figueiredo, Margarida,Carvalho, Luísa C. R.
, p. 1346 - 1350 (2018)
An efficient solid-phase synthesis appro...
Method suitable for industrial production and preparation of gefitinib
-
, (2021/08/19)
The invention discloses a method suitabl...
Synthesis of gefitinib
-
Paragraph 0021-0026, (2021/09/29)
The invention relates to preparation of ...
Purification process of gefitinib
-
Paragraph 0038; 0045-0085, (2020/08/25)
The invention provides a purification pr...
Synthesis method of tumor cell inhibition drug
-
Paragraph 0042; 0052-0053; 0054; 0064-0065, (2020/02/29)
The invention relates to the technical f...
184475-35-2 Process route
-
- 199327-61-2
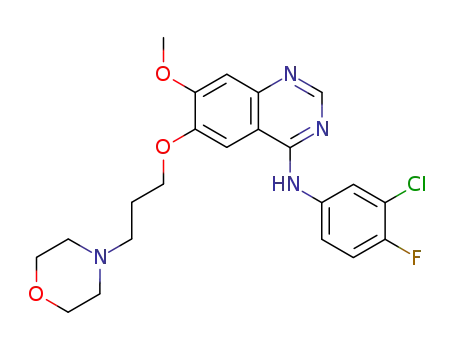
7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-one
-
- 367-21-5
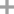
3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamine

-
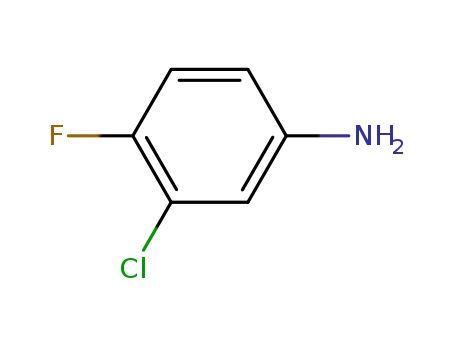
- 184475-35-2
gefitinib
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-one; With thionyl chloride; N,N-dimethyl-formamide; for 1h; Reflux;
3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamine; In isopropyl alcohol; for 1h; Reflux;
|
84% |
|
With potassium carbonate; In isopropyl alcohol; at 80 - 85 ℃; for 1h;
|
82% |
|
7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-one; With thionyl chloride; In N,N-dimethyl-formamide; for 2h; Heating;
3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamine; In N,N-dimethyl-formamide; at 100 ℃; for 1h; Further stages.;
|
73% |
|
7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-one; With triethylamine; trichlorophosphate; In toluene; at 5 - 70 ℃;
3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamine; In isopropyl alcohol; toluene; at 70 ℃; for 1h;
|
62.86% |
|
7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-one; With thionyl chloride; for 4h; Reflux;
3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamine; In i-Amyl alcohol; for 6h; Reflux;
|
-

- 367-21-5
3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamine

-
![N′-[2-cyano-5-methoxy-4-{3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy}phenyl]-N,N-dimethylformamidine](/upload/2024/4/1114f7bf-0cd5-4752-9322-33f3084fb173.png)
-
N′-[2-cyano-5-methoxy-4-{3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy}phenyl]-N,N-dimethylformamidine

-

- 184475-35-2
gefitinib
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With acetic acid; at 130 ℃; for 3h; Temperature;
|
78% |
|
With acetic acid; In 5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene; at 135 ℃;
|
71.1% |
|
With acetic acid; at 125 - 130 ℃; for 3h;
|
70% |
184475-35-2 Upstream products
-
367-21-5

3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamine
-
199327-59-8
4-chloro-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazoline
-
7357-67-7
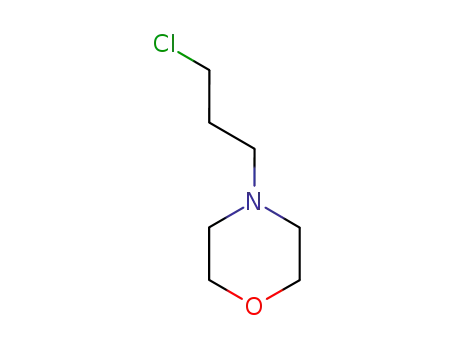
4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine
-
184475-71-6
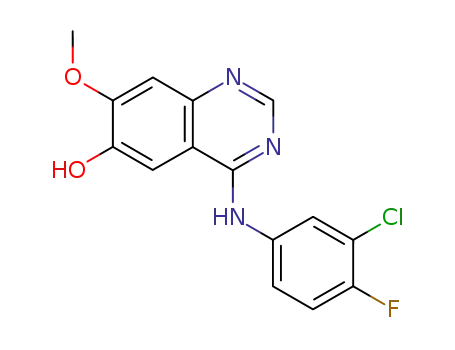
4-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamino)-6-hydroxy-7-methoxyquinazoline
184475-35-2 Downstream products
-
199327-61-2
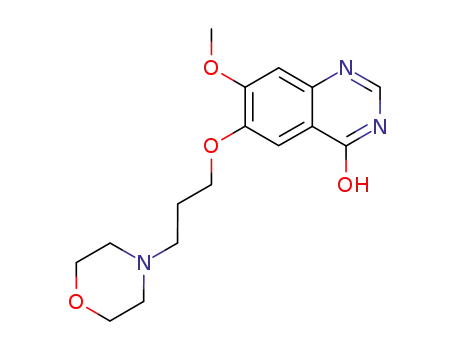
7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazolin-4-ol
-
847949-49-9
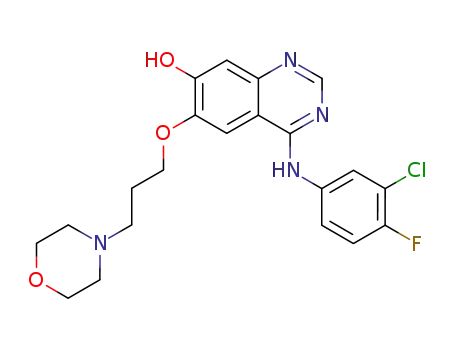
O-Demethyl-Gefitinib
-
869475-51-4
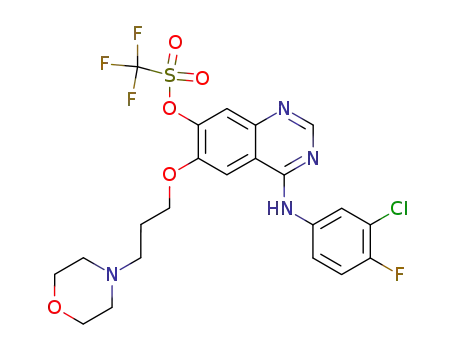
trifluoro-methanesulfonic acid 4-(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenylamino)-6-(3-morpholin-4-yl-propoxy)-quinazolin-7-yl ester
-
199327-59-8

4-chloro-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholinopropoxy)quinazoline
Relevant Products
-
3-Methyl-6-nitroindazole
CAS:6494-19-5
-
2-ethyl-5-nitroaniline
CAS:20191-74-6